Social Anxiety Disorder: Understand the Symptoms, Causes, and Diagnosis
Social anxiety disorder can quietly take control of everyday life, making simple interactions feel overwhelming and emotionally exhausting. If you constantly fear being judged, avoid social situations, or feel intense discomfort around others, you’re not alone, and you’re not weak. Social anxiety disorder is a real, diagnosable mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know: the key symptoms, early warning signs, underlying causes, how it’s diagnosed, and how it differs from general anxiety. Most importantly, you’ll gain clarity and reassurance that effective support and treatment options are available.
What Is Social Anxiety Disorder?
Social anxiety disorder (SAD), also known as social phobia, is a chronic mental health condition characterized by an intense and persistent fear of social situations. Unlike occasional nervousness, this fear doesn’t fade with time; it often worsens without support.
People with social anxiety disorder experience overwhelming worry about being judged, embarrassed, or rejected in everyday interactions such as speaking in meetings, attending social gatherings, or even making phone calls.
This condition goes beyond shyness. While shyness may cause brief discomfort, social anxiety disorder interferes with daily functioning, relationships, academic performance, and career growth. The fear is typically out of proportion to the actual situation and is difficult to control, even when the person knows their anxiety is irrational.
Social Anxiety Disorder Symptoms
Understanding social anxiety disorder symptoms is crucial for early recognition and effective support. Symptoms can appear emotionally, physically, and behaviorally—and often overlap.
Emotional and Psychological Symptoms
Intense fear of being judged or criticized
Persistent worry before, during, and after social situations
Fear of embarrassment or humiliation
Feeling extremely self-conscious around others
Physical Symptoms
Rapid heartbeat or chest tightness
Excessive sweating or trembling
Blushing, nausea, or dizziness
Shortness of breath
Behavioral Symptoms
Avoiding social interactions or public settings
Difficulty making eye contact
Cancelling plans at the last minute
Relying on substances or distractions to cope
These symptoms can significantly affect quality of life and may lead individuals to isolate themselves, reinforcing the anxiety over time.
Social Anxiety Disorder Diagnosis
A proper social anxiety disorder diagnosis can only be made by a qualified mental health professional. Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive evaluation rather than a single test.
How Social Anxiety Is Diagnosed
Detailed clinical interview to assess symptoms and history
Use of standardized anxiety assessment tools
Evaluation based on diagnostic criteria (such as frequency, intensity, and duration of symptoms)
Ruling out other mental health conditions or medical causes
To receive a diagnosis, symptoms must persist for several months and cause significant distress or impairment in social, academic, or professional functioning. Early diagnosis plays a critical role in preventing long-term emotional and social consequences.
What Causes Social Anxiety Disorder?
There is no single cause of social anxiety disorder. Instead, it usually develops due to a combination of biological, psychological, and environmental factors.
Common Causes Include
Genetics: A family history of anxiety disorders increases risk
Brain Chemistry: Heightened activity in the brain’s fear center can trigger exaggerated anxiety responses
Past Experiences: Bullying, public humiliation, or negative social experiences
Personality Traits: Perfectionism, sensitivity to criticism, or low self-esteem
Understanding what causes social anxiety disorder helps normalize the condition—it’s not a personal failure but a complex interaction of factors.
Signs of Social Anxiety Disorder
The signs of social anxiety disorder often show up gradually and may be mistaken for introversion or lack of confidence. However, these signs tend to be persistent and disruptive.
Common Warning Signs
Extreme fear of speaking in public or group settings
Avoiding social events, meetings, or presentations
Excessive self-criticism after interactions
Feeling “on edge” around unfamiliar people
Difficulty asserting opinions or setting boundaries
Recognizing these signs early can make a meaningful difference in seeking timely support and improving daily functioning.
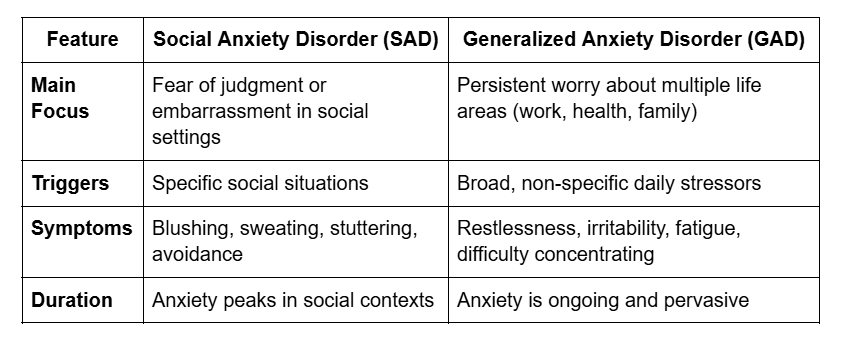
Social Anxiety Disorder vs General Anxiety
Many people confuse social anxiety disorder with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), but they are distinct conditions. Understanding the difference can help you identify the right treatment and coping strategies.
While both involve excessive anxiety, social anxiety is situation-specific, whereas generalized anxiety is persistent and wide-ranging. Correctly distinguishing between the two ensures appropriate interventions like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or exposure therapy.
How Social Anxiety Disorder Impacts Daily Life
Social anxiety disorder doesn’t just make social situations uncomfortable—it can deeply affect relationships, career, and personal growth.
Relationships: Difficulty forming or maintaining friendships or romantic relationships
Work and School: Fear of public speaking, attending meetings, or networking can limit career advancement
Everyday Activities: Avoiding parties, restaurants, or even casual conversations leads to isolation
Mental Health: Persistent anxiety can increase the risk of depression, substance use, or low self-esteem
Recognizing the impact of social anxiety disorder is the first step toward seeking treatment and regaining control over your life.
Conclusion
Social anxiety disorder is a real, manageable condition. By understanding its symptoms, causes, and differences from general anxiety, you can take informed steps toward healing. Early recognition, professional diagnosis, and appropriate interventions can dramatically improve quality of life.
If you or a loved one struggles with social anxiety, support is available. Take the first step toward recovery with personalized care and guidance through Online Social Anxiety Treatment.