Role of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Treating Sleep Disorders
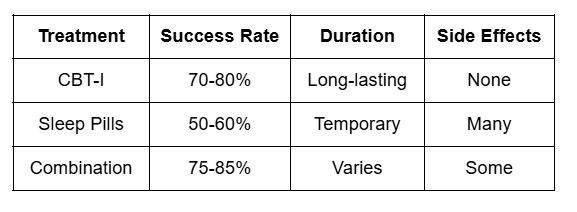
Do you struggle to fall asleep every night? Are you tired of counting sheep? Sleep disorders affect 50 to 70 million Americans today. About 30% of adults report short-term insomnia problems. Studies show 10% suffer from chronic insomnia disorder. CBT for insomnia helps 70-80% of patients improve their sleep. This therapy works better than sleeping pills long-term.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy treats sleep problems without medication. CBT-I focuses on changing thoughts and behaviors about sleep. Research shows CBT-I works in just 6-8 weeks. The therapy has no side effects like medications do. About 60% of patients reduce or stop sleep medications. Insurance companies now cover CBT-I for insomnia treatment. More doctors recommend this therapy as a first-line treatment.
This guide explains how CBT treats sleep disorders. We show the techniques that help people sleep. You will learn about treatment success rates, too. CBT offers hope for better sleep without pills. Understanding this therapy can change your sleep forever. Many people sleep better after just a few sessions.
Understanding CBT for Sleep Disorders
CBT is a proven therapy for sleep problems. It changes how people think about sleep. The therapy teaches better sleep habits, too.
What is CBT-I
CBT-I means Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia specifically. Therapists help patients identify negative sleep thoughts. The treatment addresses behaviors that prevent good sleep. Sessions focus on building healthy sleep patterns consistently. Treatment typically lasts 6 to 8 weekly sessions.
How CBT-I Works
Therapy changes unhelpful thoughts about sleep and rest. Patients learn to associate the bed with sleep only. The treatment restricts time in bed initially, sometimes. Sleep efficiency improves through structured sleep schedules daily. Relaxation techniques help calm the mind before bed. Patients track sleep patterns in daily sleep diaries.
CBT-I vs Sleep Medications
Key Components of CBT-I
CBT-I uses several proven techniques together. Each component targets different aspects of sleep. Combining these methods produces the best results.
Sleep Restriction Therapy
Patients limit their time in bed to actual sleep. This creates mild sleep debt that improves sleep. Gradually, bedtime increases as sleep improves. Most people sleep better within 2 weeks. The method increases sleep drive and efficiency naturally.
Stimulus Control Therapy
Use the bed only for sleep and intimacy
Get up if not asleep within 20 minutes
Keep a consistent wake time every single day
Cognitive Therapy
Therapy addresses worries and fears about sleep problems. Patients learn to challenge unrealistic sleep expectations daily. Negative thoughts about sleep get replaced with realistic ones. Reducing anxiety about sleep helps people fall asleep. Many insomnia patients worry too much about sleep.
Sleep Hygiene Education
Good sleep habits support CBT-I treatment success. Sleep hygiene forms the foundation of better sleep. Simple changes can make big differences quickly.
Bedroom Environment Optimization
Keep the bedroom temperature between 60 and 67 degrees Fahrenheit. Use blackout curtains to block all outside light. Remove electronic devices from the bedroom completely. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows for support. Keep the bedroom quiet or use white noise machines.
Daily Habits and Routines
Avoid caffeine after 2 PM every single day. Exercise regularly, but not close to bedtime hours. Limit alcohol intake as it disrupts sleep quality. Avoid large meals within 3 hours of bedtime. Get morning sunlight exposure for circadian rhythm regulation. Keep consistent sleep and wake times even on weekends.
What to Avoid
Don't nap during the day if possible. Avoid screen time 1 hour before bed. Don't exercise vigorously within 3 hours of sleep. Skip heavy or spicy foods before bedtime. Avoid clock-watching when trying to fall asleep. Don't try too hard to fall asleep.
Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation methods calm the mind and body. These techniques prepare you for better sleep. Regular practice improves effectiveness over time significantly.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Tense and relax muscle groups systematically throughout the body. Start with the toes and work up to the head. Hold tension for 5 seconds, then release completely. Focus attention on the difference between tense and relaxed. This reduces physical tension that prevents sleep onset. Practice this technique daily for the best results.
Deep Breathing Exercises
Breathe in slowly through the nose for 4 counts. Hold breath gently for 4 counts total. Exhale slowly through the mouth for 6 counts. Repeat this cycle 10 times before bed. Deep breathing activates the relaxation response naturally. This lowers heart rate and blood pressure.
Mindfulness Meditation
Focus attention on present moment sensations
Observe thoughts without judgment or reaction
Return focus to breath when the mind wanders
Treatment Success and Outcomes
CBT-I produces excellent results for most patients. Success rates are higher than with medication alone. Long-term improvements make CBT-I a cost-effective treatment.
Success Rates
70-80% of patients show significant improvement with treatment. Sleep efficiency increases by an average of 20-30% typically. Time to fall asleep decreases by 30-40 minutes. Total sleep time increases by 45-60 minutes. 60% of patients achieve normal sleep patterns. Improvements last 1-2 years after treatment ends.
Long-Term Benefits
Skills learned through CBT-I last a lifetime with practice. Patients handle future sleep problems better independently now. Reduced need for sleep medications saves money long-term. Better sleep improves overall health and quality of life. Mood, energy, and concentration improve with better sleep.
Who Benefits Most
People with chronic insomnia benefit most from CBT-I. Those motivated to make behavior changes succeed best. Patients willing to keep sleep diaries do better. Adults of all ages can benefit from treatment. CBT-I works for insomnia related to medical conditions. Even people on sleep medications can benefit significantly.
Getting Started with CBT-I
Finding qualified CBT-I therapists is important for success. Several options exist for accessing this treatment. Cost and availability vary by location and insurance.
Finding a Therapist
Search for certified CBT-I therapists through professional directories. Ask your doctor for referrals to sleep specialists. Check with the insurance company for covered providers. Many therapists offer CBT-I through telehealth now. Online CBT-I programs are available as an alternative option. Apps provide self-guided CBT-I for mild cases.
What to Expect
The initial session includes a detailed sleep history and assessment. The therapist will ask about sleep patterns and habits. You will start keeping a sleep diary immediately. Weekly sessions last 30-60 minutes, typically each time. Homework assignments between sessions are required. Treatment takes 6-8 weeks for most people.
Cost and Insurance Coverage
CBT-I costs $150-300 per session without insurance. Most insurance plans now cover CBT-I treatment. Medicare covers CBT-I for chronic insomnia patients. Some online programs cost less than in-person therapy. Free apps offer basic CBT-I techniques and tools. Investment pays off through better sleep and health.
Conclusion
CBT-I is a highly effective treatment for sleep disorders. The therapy works better than medications long-term. Success rates reach 70-80% for most patients treated. Techniques include sleep restriction, stimulus control, and cognitive therapy. Good sleep hygiene and relaxation methods support treatment success.
FAQs
How long does CBT-I take to work? Most people see improvement within 4 weeks of starting. Some patients notice changes in just 2 weeks. Full benefits usually appear after completing 6-8 sessions. Results continue improving even after treatment ends.
Is CBT-I better than sleeping pills? Yes, CBT-I provides longer-lasting results without side effects. Medications work fast, but their effects are temporary. CBT-I teaches skills that last a lifetime. Success rates for CBT-I are 70-80% compared to 50-60% for pills.
Can I do CBT-I on my own? Self-help books and apps are available, but therapist guidance works best. Online programs can be effective for mild cases. Severe insomnia usually needs professional help. Working with a therapist increases success rates significantly.
Does insurance cover CBT-I treatment? Most insurance plans, including Medicare, now cover CBT-I sessions. Check with your specific insurance provider for details. Many plans require prior authorization before starting treatment.
How many sessions do I need? Typical treatment is 6-8 weekly sessions with a therapist. Some people need fewer sessions for mild insomnia. Severe cases may require 10-12 sessions total. Progress is monitored through sleep diaries each week.