Emotional Burnout: Explore the Signs and Reclaim Your Emotional Energy
Emotional burnout doesn’t happen overnight; it builds quietly, draining your energy, motivation, and sense of purpose until even simple tasks feel overwhelming. You may feel constantly tired, emotionally numb, or stuck in a cycle where no amount of rest seems to help. Nowadays, emotional burnout has become increasingly common, affecting people across careers, relationships, and life stages.
The good news is that emotional burnout is not a personal failure, and it is not permanent. By understanding what emotional burnout really is, recognizing its early warning signs, and learning how to recover effectively, you can regain emotional clarity, restore balance, and begin feeling like yourself again.
What Is Emotional Burnout?
Emotional burnout is a state of deep emotional, mental, and physical exhaustion caused by prolonged and unmanaged stress. Unlike ordinary tiredness, emotional burnout doesn’t disappear after a good night’s sleep or a short break. It leaves you feeling drained, detached, and unable to cope with daily responsibilities the way you once did.
People experiencing emotional burnout often describe feeling empty, overwhelmed, or trapped, as though they have nothing left to give. Over time, this persistent state of stress can begin to affect your health, relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life.
Emotional burnout is not a sign of weakness; it is a signal that your mind and body have been under pressure for too long without adequate recovery.
Emotional Burnout vs. Emotional Exhaustion
Although the terms are often used interchangeably, emotional exhaustion and emotional burnout are not exactly the same.
Emotional exhaustion refers to the feeling of being emotionally drained due to stress. It is often one of the earliest and most noticeable signs of burnout.
Emotional burnout, on the other hand, is a broader and more severe condition. It includes emotional exhaustion but also involves:
Loss of motivation
Emotional detachment
Reduced sense of accomplishment
Feelings of hopelessness or apathy
In simple terms, emotional exhaustion is a warning sign, while emotional burnout is what happens when that warning goes unaddressed for too long.
Common Symptoms of Emotional Burnout
Emotional burnout affects people differently, but the symptoms generally fall into three main categories: emotional, physical, and behavioral.
Emotional Symptoms of Emotional Burnout
Persistent feelings of hopelessness or emptiness
Loss of motivation and enthusiasm
Increased irritability or frustration
Emotional numbness or detachment
Heightened cynicism or pessimism
Feeling stuck, trapped, or powerless
You may notice that things you once cared deeply about no longer bring satisfaction or meaning.
Physical Symptoms of Emotional Burnout
Chronic fatigue, even after resting
Frequent headaches or muscle tension
Changes in appetite (overeating or loss of appetite)
Sleep disturbances or insomnia
Lowered immunity and frequent illness
Digestive problems or unexplained aches
Because emotional burnout keeps the body in a prolonged stress response, physical symptoms often intensify over time.
Behavioral Symptoms of Emotional Burnout
Withdrawing from work, responsibilities, or social interactions
Procrastination or declining performance
Avoiding communication with others
Increased reliance on food, alcohol, or substances to cope
Coming to work late or leaving early
These behaviors are often misunderstood as laziness or disinterest, when they are actually signs of emotional overload.
What Causes Emotional Burnout?
Emotional burnout develops when stress becomes constant, and recovery becomes rare. While everyone experiences stress, emotional burnout occurs when stress is chronic, unrelenting, and emotionally demanding.
Common Everyday Causes of Emotional Burnout
Ongoing financial stress
Relationship conflicts
Parenting pressures
Caregiving responsibilities
Lack of personal time or boundaries
Even stressors that seem manageable at first can accumulate and lead to burnout if they persist long enough.
Work-Related Causes of Emotional Burnout
High-pressure or emotionally demanding jobs
Long working hours with little rest
Lack of control or autonomy
Feeling undervalued or unappreciated
Poor work-life balance
Professions such as healthcare, teaching, caregiving, and customer service are especially associated with emotional burnout due to constant emotional output and responsibility.
Personal and Life-Related Stressors
Chronic illness or injury
Loss of a loved one
Divorce or prolonged relationship strain
Major life transitions
Living with ongoing uncertainty or instability
What triggers emotional burnout varies from person to person. What overwhelms one individual may be manageable for another, depending on support systems, coping skills, and life circumstances.
Stages of Emotional Burnout
Emotional burnout doesn’t happen suddenly, it develops gradually through identifiable stages.
1. Honeymoon Phase
High motivation and commitment
Willingness to push through stress
Ignoring early signs of fatigue
2. Onset of Stress
Increased anxiety and exhaustion
Difficulty concentrating
Reduced satisfaction and productivity
3. Chronic Stress
Persistent fatigue and irritability
Sleep disturbances
Emotional withdrawal
4. Emotional Burnout
Emotional numbness
Feelings of hopelessness and detachment
Loss of purpose and motivation
5. Habitual Burnout
Long-term mental and physical health issues
Increased risk of depression and anxiety
Difficulty functioning without significant intervention
Recognizing burnout in the earlier stages can make recovery much faster and more effective.
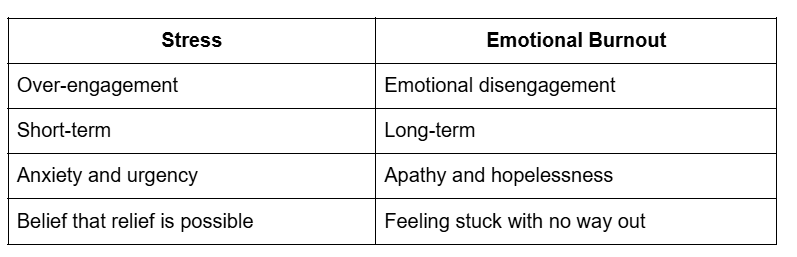
Emotional Burnout vs. Stress: What’s the Difference?
Stress and emotional burnout are closely related, but they are not the same. Understanding the difference is essential for proper recovery.
Stress is typically associated with too much pressure. When you’re stressed, you may feel overwhelmed, anxious, or tense, but you still believe that once things settle down, you’ll feel better.
Emotional burnout, however, is about emotional depletion. Instead of feeling overwhelmed, you feel empty. Motivation fades, hope diminishes, and even rest doesn’t seem to restore your energy.
If stress feels like drowning in responsibilities, emotional burnout feels like you’ve dried up completely.
Emotional Burnout vs. Depression
Emotional burnout and depression can look very similar, and in some cases, burnout can lead to depression if left untreated. However, there are important distinctions.
Emotional burnout is usually linked to specific external stressors, such as work, caregiving, or ongoing responsibilities. The negative emotions often improve when the stressor is reduced or removed.
Depression, on the other hand, is a medical condition that affects nearly every area of life. Feelings of sadness, emptiness, or hopelessness persist regardless of external circumstances and often require professional treatment.
While burnout may resolve with lifestyle changes and stress management, depression typically requires therapy, medication, or both. If emotional numbness, hopelessness, or lack of interest continues even after reducing stress, professional support is strongly recommended.
Effects of Emotional Burnout on Mental and Physical Health
When emotional burnout goes unaddressed, it can have serious consequences for both mental and physical well-being.
Physical Effects of Emotional Burnout
Chronic stress keeps the body in a prolonged fight-or-flight state, leading to:
Elevated cortisol levels
High blood pressure and heart palpitations
Digestive problems
Weight gain or weight loss
Frequent headaches and muscle pain
Over time, this constant physiological stress weakens the immune system and increases vulnerability to illness.
Mental and Emotional Effects
Increased anxiety and panic symptoms
Depression and emotional numbness
Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
Low self-esteem and self-doubt
Feelings of helplessness or hopelessness
These mental effects often reinforce burnout, creating a cycle that becomes harder to break without intervention.
Impact on Relationships and Social Life
Emotional burnout doesn’t only affect the individual, it affects those around them as well. Common relationship challenges include:
Emotional withdrawal from loved ones
Increased irritability and conflict
Reduced empathy and patience
Avoidance of social interaction
This social isolation can further intensify feelings of loneliness and emotional exhaustion.
How to Recover from Emotional Burnout?
Recovery from emotional burnout is possible, but it requires intention, patience, and self-compassion.
1. Acknowledge That You’re Experiencing Emotional Burnout
The first step toward recovery is honesty. Recognizing that you are emotionally burned out, without guilt or self-judgment, creates space for healing.
Burnout is not a personal failure. It is a natural response to prolonged stress.
2. Identify the Root Cause
Take time to reflect on what is contributing to your burnout. Ask yourself:
Is my stress coming from work, relationships, or health?
Am I carrying responsibilities that exceed my capacity?
Have I been ignoring my own needs?
Journaling or speaking with a trusted person can help clarify these stressors.
3. Reduce or Eliminate Stressors Where Possible
While not all stress can be removed, some stressors can be reduced by:
Setting clear boundaries
Delegating responsibilities
Adjusting workloads
Saying no without guilt
Small changes can create meaningful relief over time.
4. Prioritize Rest and Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for emotional recovery. Establish a consistent sleep routine, limit screen time before bed, and allow yourself adequate rest without self-criticism.
Rest is not a reward; it is a requirement.
5. Practice Mindfulness and Stress-Reduction Techniques
Mindfulness helps bring awareness back to the present moment, reducing mental overload. Effective practices include:
Meditation
Deep breathing exercises
Gentle yoga or stretching
Spending time in nature
Journaling thoughts and emotions
These practices calm the nervous system and support emotional balance.
6. Support Your Physical Health
Your emotional health is closely tied to your physical well-being. Focus on:
Eating balanced, nourishing meals
Staying hydrated
Engaging in gentle, regular movement
Avoiding excessive caffeine or alcohol
Even small, consistent habits can improve energy and mood.
7. Reconnect with Support Systems
Talking to someone you trust can relieve emotional pressure. You don’t need solutions; just being heard can make a difference.
If available, consider:
Trusted friends or family members
Support groups
Workplace assistance programs
8. Seek Professional Help When Needed
If emotional burnout feels overwhelming or persistent, professional support can be life-changing. Therapists can help with:
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
Stress management strategies
Emotional regulation tools
Seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness.
How to Prevent Emotional Burnout?
Prevention starts with awareness and self-care:
Recognize early warning signs
Maintain healthy boundaries
Schedule regular breaks and downtime
Build routines that support emotional resilience
Prioritize self-care without guilt
Addressing burnout early prevents long-term consequences.
The Bottom Line
Emotional burnout is a serious but manageable condition. It develops gradually, affects every aspect of life, and signals the need for change, not failure. With awareness, support, and intentional care, recovery is not only possible but empowering.
Listening to your emotional limits today can protect your well-being for years to come.