Is Behavioral Health the Same as Mental Health? Here’s the Truth You Need to Know
If you’ve ever searched for therapy, counseling, or wellness services, you’ve likely seen the terms behavioral health and mental health used as if they mean the same thing. This can be confusing and even overwhelming, especially when you’re trying to make the right decision for yourself or a loved one.
The truth is, while these terms are closely connected, they are not identical. Exploring the difference between behavioral health and mental health can help you choose the right type of care, get better results from treatment, and feel more confident about your healthcare decisions.
In this guide, we’ll clearly explain what each term means, how they overlap, and why the distinction truly matters.
What Is Mental Health?
Mental health refers to a person’s overall emotional, psychological, and cognitive well-being. It influences how individuals think, feel, process emotions, handle stress, relate to others, and make decisions in everyday life. Mental health is not just the absence of illness; it also includes emotional resilience, self-esteem, and the ability to cope with life’s challenges.
When mental health is balanced, people can function effectively at work, maintain relationships, and adapt to change. When it’s compromised, daily functioning, motivation, and quality of life can be significantly affected.
Common Mental Health Conditions
Mental health conditions typically involve changes in mood, thinking, or perception. Some of the most common include:
Depression
Anxiety disorders
Bipolar disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Schizophrenia
These conditions may develop due to genetics, brain chemistry, trauma, stress, or life experiences.
Mental Health Treatment Options
Mental health care often focuses on improving emotional regulation and thought patterns. Common treatments include:
Psychotherapy or talk therapy
Psychiatric medications
Individual or group counseling
Crisis intervention and emotional support
What Is Behavioral Health?
Behavioral health is a broader concept that examines how human behaviors impact overall well-being, including mental, emotional, and physical health. It looks at habits, actions, and lifestyle choices that can either support or harm a person’s health over time.
While mental health focuses on internal emotional states, behavioral health emphasizes patterns of behavior, especially those that influence health outcomes.
Common Behavioral Health Conditions
Behavioral health conditions often involve repeated behaviors that interfere with daily life or health, such as:
Substance use and addiction
Eating disorders
Gambling disorders
Stress-related behaviors
Sleep and lifestyle behavior issues
These behaviors may be linked to underlying mental health concerns, but the primary focus is on changing harmful habits and reinforcing healthier ones.
Behavioral Health Treatment Approaches
Behavioral health care aims to modify behaviors and improve coping strategies. Treatment options often include:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Addiction counseling and recovery programs
Behavior modification therapy
Group therapy and peer support
Preventive behavioral interventions
Behavioral Health vs Mental Health
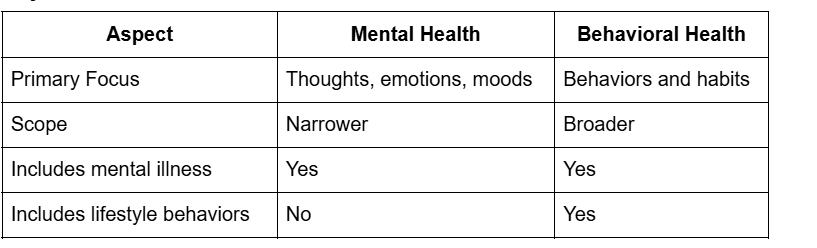
Although behavioral health and mental health overlap, they are not the same. The key difference lies in focus and scope.
Mental health concentrates on emotional and psychological conditions, while behavioral health looks at how behaviors, both positive and negative, affect a person’s overall well-being.
Key Differences at a Glance
In simple terms, mental health is part of behavioral health, but behavioral health goes beyond mental illness to include everyday behaviors that shape long-term health.
Is Behavioral Health the Same as Mental Health?
No, behavioral health is not the same as mental health, but they are deeply connected.
Mental health focuses on emotional and psychological conditions, while behavioral health includes mental health plus behaviors like substance use, eating patterns, stress management, and coping habits. This broader approach allows healthcare providers to treat the whole person, not just symptoms.
Why the Confusion Between Behavioral Health and Mental Health?
It’s common for people to confuse behavioral health and mental health because of overlapping terminology used in healthcare and insurance. Many clinics and providers use “behavioral health” as an umbrella term, which includes mental health, substance use, and behavioral interventions. This overlap often leads to misunderstanding about what type of care to seek.
Additionally, the same providers, therapists, psychologists, counselors, and social workers often address both behavioral and mental health concerns, which reinforces the perception that the terms are interchangeable.
When Should You Seek Mental Health Care vs Behavioral Health Care?
Understanding the distinction can help you get the most effective care.
Seek Mental Health Care If You Are Experiencing:
Persistent sadness, hopelessness, or anxiety
Mood swings or irritability
Psychotic symptoms, such as hallucinations
Emotional distress without clear behavioral triggers
Seek Behavioral Health Care If You Are Experiencing:
Addiction or substance misuse
Unhealthy eating or sleeping habits
Stress-related behaviors that impact health
Behavioral patterns that interfere with work, school, or relationships
How Behavioral Health and Mental Health Work Together?
Modern healthcare increasingly focuses on integrated care, where mental and behavioral health services are combined to treat the whole person. By addressing both psychological conditions and behaviors that affect health, providers can deliver more comprehensive, lasting solutions.
Benefits of Integrated Care:
Improved long-term outcomes for patients
Reduced relapse rates in mental health and addiction treatment
Enhanced quality of life
Holistic approach tailored to each individual
Final Thoughts
While closely related, behavioral health and mental health are not the same. Mental health focuses on emotions, thoughts, and psychological well-being, whereas behavioral health examines how behaviors, habits, and lifestyle choices affect overall health.
Understanding this distinction empowers you to seek the right type of care from Serenity Telehealth, make informed decisions, and improve both your mental and physical well-being. By addressing both mental health and behaviors together, you can achieve lasting, holistic wellness.
FAQs
Q: Is behavioral health better than mental health?
Ans: No. Behavioral health is broader and includes mental health, but both are equally important and work best together.
Q: Does behavioral health include mental illness?
Ans: Yes. Mental health conditions fall under behavioral health, but behavioral health also addresses lifestyle and habit-related issues.
Q: Are therapists considered behavioral health providers?
Ans: Yes. Therapists, counselors, and psychologists often treat both behavioral and mental health conditions.
Q: Is behavioral health covered by insurance?
Ans: Most insurance plans cover behavioral health services, including therapy, counseling, and mental health treatment.