PTSD vs Trauma
Do you know the difference between PTSD and trauma? Many people often confuse these two terms. About 70% of adults experience trauma in their lifetime. Only 6% of those develop PTSD, according to research. Understanding the difference helps with proper treatment and support. Trauma affects 223 million Americans each year nationwide. PTSD impacts about 13 million Americans currently living today.
Trauma is a normal response to bad events. PTSD is a mental health disorder that needs treatment. All PTSD starts with trauma, but not all trauma becomes PTSD. The brain processes trauma differently in each person naturally. Time frames and symptoms help tell them apart clearly. About 8 out of 100 people will have PTSD at some point. Women are twice as likely to develop PTSD as men.
This guide explains PTSD vs trauma in simple terms. We show the difference between PTSD and trauma clearly. You will learn if you can have trauma without PTSD. Understanding these differences improves mental health care for everyone. Proper diagnosis leads to better treatment outcomes always. Knowledge helps reduce stigma around mental health issues today.
What is Trauma
Trauma is the emotional response to a bad event. It happens to many people during their lives. The experience can be brief or last longer.
Definition of Trauma
Trauma occurs when someone experiences a deeply traumatic event. The event overwhelms a person's ability to cope. It can be physical, emotional, or psychological harm. Trauma affects how the brain processes memories. Common causes include accidents, violence, or natural disasters. The body responds with fight, flight, or freeze reactions.
Types of Trauma
Acute trauma results from a single bad event. Chronic trauma involves repeated and long exposure to events. Complex trauma comes from multiple bad events over time. Developmental trauma happens during childhood and affects growth. Medical trauma can occur from serious illness or procedures.
Common Trauma Responses
Shock and denial are immediate reactions to trauma. Emotional reactions include fear, anger, sadness, and confusion. Physical symptoms may include fatigue, headaches, and rapid heartbeat. Behavioral changes might involve withdrawal or mood swings. These responses are normal and usually go away over time.
What is PTSD
PTSD is a mental health disorder that develops after trauma. Not everyone who experiences trauma develops PTSD. It needs specific symptoms that last over time.
PTSD Definition and Diagnosis
PTSD stands for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, which is officially recognized. It develops when trauma symptoms persist beyond one month. The disorder interferes with daily life and functioning a lot. Diagnosis needs exposure to actual or threatened death or injury. Four symptom clusters must be present for diagnosis.
PTSD Symptoms and Duration
Intrusive memories include flashbacks and bad dreams repeatedly. Avoidant behaviors involve staying away from trauma reminders. Negative thoughts about self and the world persist. Hyperarousal symptoms include being easily startled and irritable. Symptoms must last longer than one month for diagnosis.
Risk Factors for Developing PTSD
Intensity and duration of trauma increase PTSD risk. Previous trauma exposure makes PTSD more likely to develop. Lack of social support after trauma raises risk. Family history of mental health issues increases vulnerability. Childhood trauma or abuse predisposes people to PTSD. Additional life stress during recovery complicates the healing process.
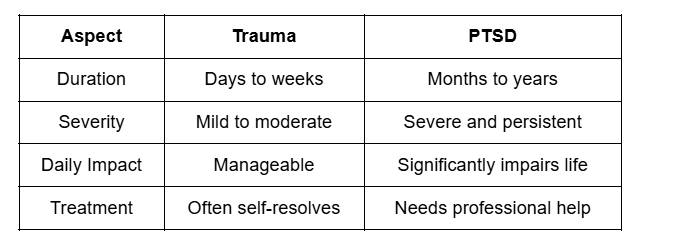
Difference Between PTSD and Trauma
Understanding key differences helps with proper identification and treatment. Trauma is universal, while PTSD is a disorder.
Duration and Timeline
Trauma responses usually last days to weeks after the event. Most people recover within three months naturally without help. PTSD symptoms persist for months or years without treatment. A PTSD diagnosis requires symptoms lasting over one month. Acute stress disorder occurs between three days and to month.
Symptom Severity and Impact
Functional Impairment Differences
Trauma allows people to continue normal daily activities. PTSD makes it difficult to maintain jobs or relationships. Trauma victims can process emotions with support slowly. PTSD sufferers struggle with emotional regulation constantly every day. Social functioning remains relatively intact with trauma alone.
Can You Have Trauma Without PTSD
Yes, most people experience trauma without developing PTSD. This is the normal and expected outcome.
Normal Trauma Recovery
Most trauma survivors recover naturally within three months. The brain processes bad memories over time successfully. Social support helps people heal from trauma faster. Talking about the experience aids in processing emotions. Engaging in normal activities promotes recovery and resilience.
Factors That Prevent PTSD Development
A strong social support network protects against PTSD development. Healthy coping mechanisms help process trauma successfully. Previous positive experiences build resilience against mental health issues. Immediate support after trauma reduces PTSD risk a lot. A sense of control during recovery promotes better outcomes.
When to Seek Professional Help
Symptoms persist beyond one month after a bad event
Daily functioning is significantly impaired by trauma symptoms
Thoughts of self-harm or suicide appear regularly
Treatment Options
Both trauma and PTSD benefit from proper treatment approaches. Early help improves outcomes for both conditions a lot.
Trauma Treatment Approaches
Trauma-focused therapy helps process difficult emotions and memories. Support groups provide a connection with others who understand. Self-care includes exercise, sleep, and healthy eating habits. Mindfulness and relaxation techniques reduce stress and anxiety. Maintaining routines provides stability during the recovery period.
PTSD Treatment Methods
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy helps change negative thought patterns. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing processes bad memories. Prolonged Exposure Therapy slowly confronts trauma-related fears safely. Medications like antidepressants may help manage symptoms effectively.
Self-Help Strategies
Regular exercise reduces stress and improves mood naturally. Establishing sleep routines helps combat insomnia and nightmares. Avoiding alcohol and drugs prevents worsening of symptoms. Connecting with supportive friends and family aids recovery. Learning stress management techniques provides coping tools daily.
Supporting Someone with Trauma or PTSD
Supporting loved ones' needs requires patience and understanding always. Different approaches help trauma versus PTSD recovery best.
How to Help Trauma Survivors
Listen without judgment when they want to talk. Give them space if they need time alone. Offer practical help with daily tasks and responsibilities. Avoid pressuring them to talk before ready. Maintain normal routines and activities when possible. Be patient as recovery takes time and varies. Encourage professional help if symptoms persist beyond weeks.
Supporting Someone with PTSD
Learn about PTSD to understand their experience better. Recognize triggers and help avoid or manage them. Encourage treatment and offer to help find resources. Be patient with mood swings and emotional reactions. Maintain boundaries while offering consistent support always. Celebrate small victories and progress in the recovery journey.
When to Encourage Professional Treatment
Symptoms worsen or do not improve over time. Daily functioning continues to decline a lot over the weeks. Relationships suffer due to trauma or PTSD symptoms. Self-harm thoughts or behaviors appear at any time. Substance abuse develops as a coping mechanism for pain. Quality of life is significantly impaired for extended periods.
Conclusion
PTSD and trauma are different but related conditions. Trauma is a normal response, while PTSD is a disorder. Most people recover from trauma without developing PTSD. Understanding differences helps with proper treatment and support. Professional help is available and effective for both. Early help prevents trauma from becoming chronic PTSD. Knowledge reduces stigma and promotes healing for everyone.
FAQs
What is the main difference between PTSD and trauma? Trauma is a normal response to bad events. PTSD is a mental health disorder that needs treatment. All PTSD starts with trauma. Not all trauma becomes PTSD.
Can you have trauma without getting PTSD? Yes, most people experience trauma without developing PTSD. About 94% of trauma survivors do not get PTSD. This is the normal and expected outcome. Recovery happens naturally within weeks or months.
How long does trauma last compared to PTSD? Trauma usually lasts days to weeks after the event. Most people recover within three months naturally. PTSD symptoms persist for months or years. PTSD needs symptoms lasting over one month.
What percentage of trauma survivors develop PTSD? Only about 6% of trauma survivors develop PTSD. This means 94% recover without developing a disorder. Women are twice as likely to develop PTSD. Risk factors affect who develops the disorder.
When should you seek help for trauma? Seek help if symptoms last over one month. Get help if daily life is significantly impaired. Early help prevents trauma from becoming PTSD. Professional treatment improves recovery outcomes greatly.